Key CR Topics
Important CR topics identified for Hermes in a multi-stage process

The basic prerequisite for systematic and targeted corporate responsibility management lies in identifying and becoming aware of key CR issues. In order to achieve this, Hermes Germany carried out a multi-stage materiality analysis along the entire value chain.
For its materiality analysis of CR topics, Hermes Germany drew on the Otto Group's ‘impACT’ process, winner of the German government's CSR Prize in 2014. impACT links the assessment of an impact with the action derived from it in order to define adequate and effective CR strategies. The Otto Group has used this management process to fundamentally change the way in which the impact of its business activities on people and nature is determined, evaluated, and how effective and efficient measures are derived from it.
Detailed materiality analysis
For the materiality analysis, we first identified the environmental and social impacts caused by the business activities of the Hermes Group as a whole through its respective individual companies. The entire value chain was taken into consideration: from sourcing logistics (importing and exporting goods in cooperation with contractual partners such as freight forwarders, airlines, shipping companies) through to Hermes sites and distribution logistics (the transport of shipments on the line haul and the final mile, i.e. the delivery of parcels to customers mainly in cooperation with contractual partners). The effects caused by our contractual partners were also taken into account.
Subsequently, we conducted a quantitative evaluation of the ecological and social impact identified. We evaluated the extent of the environmental impact in external costs, and used various indicators to measure the social impact, such as wages, occupational safety and working hours. In addition to this quantitative evaluation, an employee survey was conducted at Hermes Germany to assess the relevance of the respective social and ecological impacts with regard to stakeholder expectations.
Results of materiality assessment by value added
At the end of the materiality analysis, we compared the quantitative extent of our respective ecological and social impact with the assessment of relevance from a stakeholder perspective. We combined the results in a so-called materiality matrix for the Hermes Group (see chart).
The effects with the highest priority for Hermes are those for which a very high degree of materiality exists both in terms of the quantitative effects and in terms of stakeholder expectations. As can be seen from the materiality matrix, Hermes' greatest challenges lie in the distribution value chain, where climate gases, pollutants, wages and working hours have the highest priority.
Hermes Germany’s CR strategy was based on this materiality analysis. Strategic objectives have been designed to address the key challenges and ensure that measures have the greatest possible impact.
Materiality matrix across the Hermes Group's value creation levels
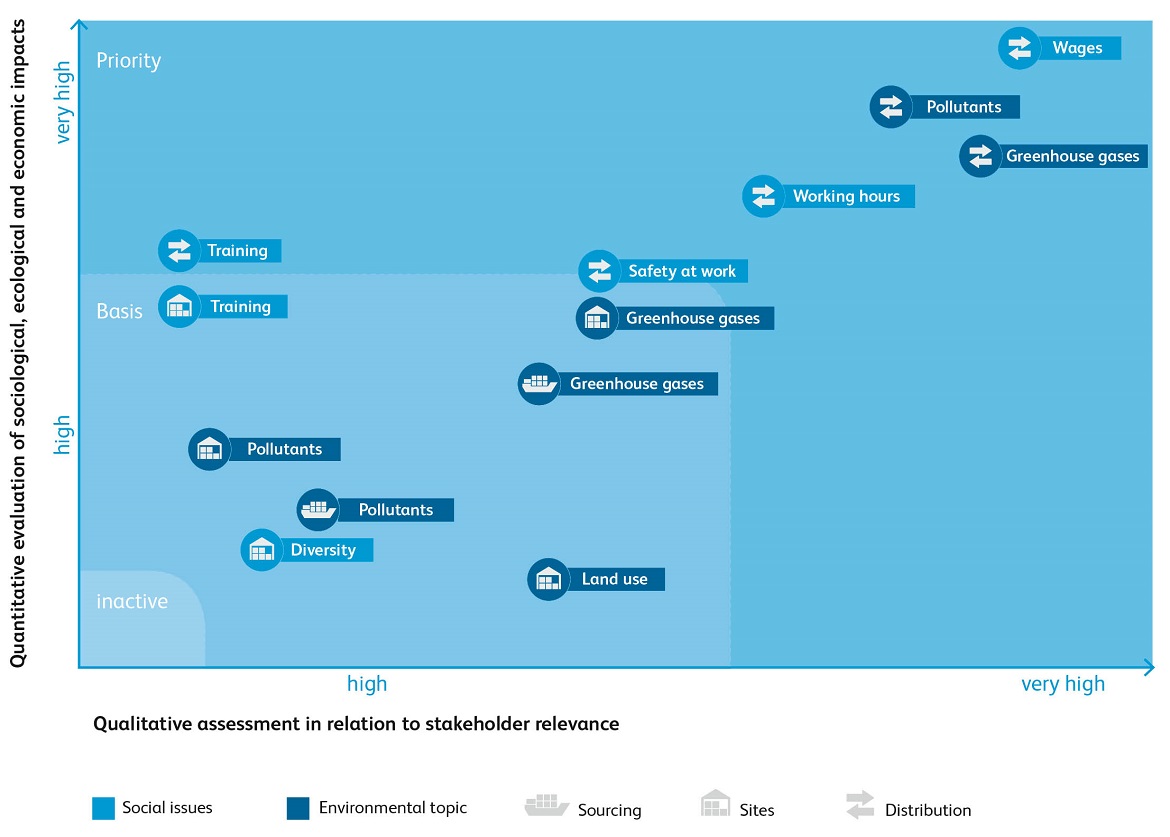
When it comes to the environment, greenhouse gases and pollutants have the highest priority. Hermes Germany has tailored the core of its CR strategy to this. Reductions in greenhouse gases and pollutants can be actively achieved above all in distribution logistics and at our sites. However, Hermes Germany and Hermes International, newly founded in March 2018, are also active in the field of sourcing logistics, for example through initiatives. This is largely because in sourcing we cooperate primarily with external contractual partners such as airlines or shipping companies.
Other environmental issues such as water consumption and land use at our sites are less serious in the overall context of Hermes Germany, but we are not ignoring them. On the contrary: since 1999, we have been implementing ISO 14001 certification for our sites. This globally applicable environmental management standard requires us to continuously improve our environmental management. We also work closely with the German Nature and Biodiversity Conservation Union (NABU) as a cooperation partner to reduce, and compensate for, the impact on nature that occurs when constructing new buildings. In the Climate & Environment section we describe in detail the measures undertaken and successes achieved.
In the Service & Clients section, we explore the significant importance of environmental aspects such as the topics of greenhouse gases and pollutants. The ecological evaluation of suppliers, energy saving measures and the reduction of emissions are important focal points.
The materiality matrix also shows the high relevance of social issues. Five important areas are mentioned: remuneration, safety at work, working time, diversity and training. Hermes Germany pays particular attention to all these points in its CR strategy. The social topics are considered in the Work & Life section. The most highly rated topics of remuneration, safety at work and working hours primarily concern distribution logistics and have the highest priority there. This applies above all to fair pay. The ongoing training of our staff at our sites and in distribution represents an opportunity for us and the issue of diversity is also being targeted at Hermes sites.
Report structure
The following two tables explain the structure and organisation of the three subject areas of the report: Service & Clients, Work & Life and Climate & Environment. The main topics for Hermes Germany and Hermes Einrichtungs Service are explained using the corresponding GRI standards in the particularly important internal (sites, distribution) and external areas (partners).
The central CR topics identified by the materiality analysis - greenhouse gases, pollutants and social issues - are thus reflected in the reporting structure of the CR Report. They have been assigned to the corresponding GRI standards.
Measures on the first two main issues of greenhouse gases and pollutants can be found in the Service & Clients and Climate & Environment sections, while the strategies on the five important social topics are presented in the Work & Life section.
Service & Clients and Climate & Environment
| Key issues for Hermes | Corresponding GRI standards | Particularly important areas |
| Greenhouse gases | Energy, Emissions, Ecological evaluation of suppliers |
|
| Pollutants | Emissions, Ecological evaluation of suppliers |
|
Work & Life
| Key issues for Hermes | Corresponding GRI standards | Particularly important areas |
| Working time | Supplier evaluation (social), Human rights |
|
| Safety at work | Occupational health and safety |
|
Appropriate remuneration | Supplier evaluation (social) |
|
| Training and development | Training and development |
|
| Diversity | Diversity and equal opportunities |
|





